How does a boiler contribute to the efficiency in a steam power plant?
A boiler plays a crucial role in the efficient and functional operation of a steam power plant. It acts as the heart of the power generation process, converting heat energy into high-pressure steam that drives turbines to produce electricity.The inclusion of a boilers significantly enhances the efficiency and functionality of a steam power plant in several ways:
Heat Transfer Efficiency: Boilers are designed to maximise heat transfer from the combustion process to the water, ensuring that the heat generated is efficiently utilised to produce steam. This efficient heat transfer contributes to overall plant efficiency and reduces fuel consumption.
Steam Generation Control: Boilers precisely control the steam pressure and temperature, providing a consistent supply of steam to the turbines. This control is essential for maintaining stable and efficient power generation.
Steam Quality Assurance: Boilers remove impurities from the water and maintain the purity of the steam, preventing corrosion and damage to the turbines and other components. This ensures the longevity and reliability of the power plant.
Fuel Flexibility: Boilers can be designed to utilise various fuel sources, including coal, natural gas, oil, or even biomass. This flexibility allows power plants to adapt to changing fuel prices and availability, ensuring a reliable power supply.
Co-generation Potential: Boilers can be combined with other systems to provide co-generation, producing both electricity and heat simultaneously. This efficient use of energy reduces overall fuel consumption and environmental impact.
Boilers are essential components of steam power plants, enabling efficient electricity generation through controlled heat transfer, steam quality
What is Steam Power Plant ?
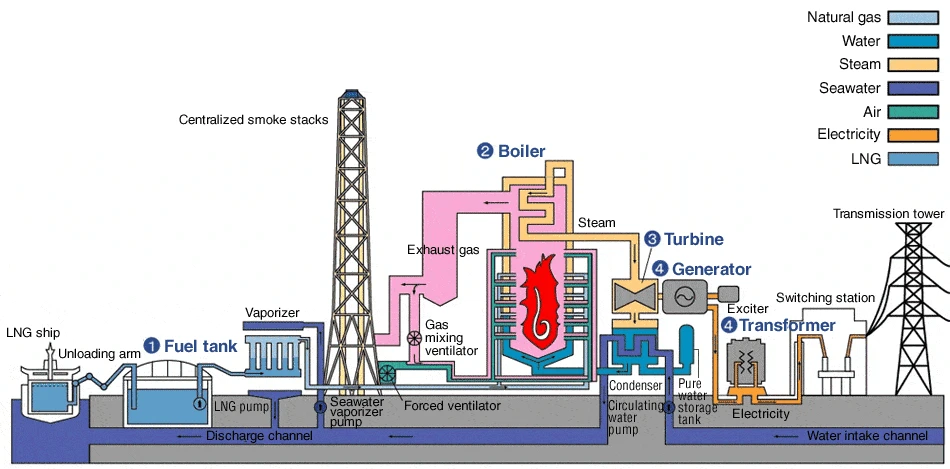
A steam power plant, also known as a steam power plant , is a facility designed to generate electricity through the use of steam as the primary working fluid. It operates based on the principles of thermodynamics, utilizing the conversion of heat energy into mechanical work and subsequently into electrical energy. The primary components of a steam power plant include a boiler, a turbine, a condenser, and a generator.
Here’s a breakdown of the key components and their functions within a steam power plant:
Boiler: The boiler is responsible for heating water to generate steam. This is typically achieved by burning fossil fuels (such as coal, oil, or natural gas) or by using nuclear energy. The generated steam is at high pressure and temperature.
Turbine: The high-pressure steam from the boilers is directed into a turbine. The turbine is designed with blades that are turned by the force of the steam’s high-speed flow. As the steam flows through the turbine, its high-pressure energy is converted into rotational mechanical energy.
Generator: The turbine is connected to a generator, which consists of coils of wire within a magnetic field. As the turbine spins, it turns the rotor of the generator, creating a moving magnetic field. This movement induces an electric current in the wire coils, ultimately producing electrical energy.
Condenser: After passing through the turbine, the steam is directed to the condenser. Here, the steam is cooled and condensed back into water, releasing its latent heat. This process allows for the efficient reuse of the water in the boiler, reducing water consumption and increasing overall efficiency.
Cooling System: Steam power plants require a cooling system to dissipate excess heat from the condenser. This can involve cooling water from nearby water bodies, cooling towers, or other heat exchange methods.
The electricity generated by the generator is then transmitted through power lines to homes, businesses, and industries, where it serves as a source of electrical power.
Steam power plants have been a significant source of electricity generation for many years due to their reliability and the scalability of their design. However, their environmental impact and reliance on fossil fuels have led to increased interest in cleaner and more sustainable alternatives, such as renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power.
A steam power station, also known as a coal-fired power plant, harnesses the heat energy generated from burning coal to produce a significant amount of electrical energy. These types of power stations are widely utilized across the globe due to the abundant availability of coal, which enables them to generate electricity on a large scale.
Steam Power Plant Diagram
In most countries, steam power plants are commonly utilized as baseload power plants due to their reliable and consistent electricity generation capacity. These power plants operate by producing steam through the combustion of fossil fuels or nuclear reactions, which in turn drives turbines connected to generators to produce electricity. The process of starting and stopping steam power plants can be time-consuming and requires careful management.
Due to their heavy and intricate infrastructure, steam power plants are not suitable for catering to frequent and short-term peak loads. High-volume keyword demands from rapid and substantial increases in electricity consumption, such as during periods of extreme weather conditions or when there is a surge in industrial activity, cannot be efficiently met by steam power plants alone. Meeting such demand requires power plants that are capable of quick and flexible responses.
To address these high-volume demands, countries often rely on a mix of power generation sources. Alongside baseload steam power plants, they incorporate other types of power plants like natural gas-fired plants, hydroelectric plants, and renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. These additional sources offer faster startup times, enabling them to swiftly respond to sudden spikes in electricity consumption.
By diversifying the energy mix and incorporating power plants designed to handle high-volume keyword requirements, countries can ensure a more resilient and stable power grid. This approach allows for efficient and sustainable electricity generation while effectively addressing both the consistent demands of baseload power and the intermittent demands of peak load situations.
Factors to Determine the Site of Steam Power Plant
Steam power plant stations keep on working very close to full efficiency for 24 hours a day. Power Plants have a standard life of 30 to 40 years. The following is a record of factors that affect the selection of a site for building a Steam power station:
Supply of fuel:
Steam power stations are a major source of electricity generation in many countries. They use coal, oil, or natural gas to heat water to produce steam, which drives a turbin generate electricity. The amount of fuel required by a steam power station varies depending on its size and efficiency, but it can be significant. For example, a large coal-fired power plant may consume up to 10,000 tons of coal per day.
The high volume of fuel required by steam power stations means that it is important to locate them close to sources of fuel. This helps to reduce the transportation costs of fuel, which can be a significant expense. In some cases, steam power stations may be located near coal mines, which can provide a reliable and cost-effective source of fuel.
The use of coal and oil as fuel for steam power stations has a number of environmental impacts. These include air pollution, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. Air pollution from coal-fired power plants can cause a variety of health problems, including respiratory illnesses, heart disease, and cancer. Water pollution from coal-fired power plants can damage aquatic ecosystems and contaminate drinking water supplies. Greenhouse gas emissions from coal-fired power plants contribute to climate change.
There are a number of ways to reduce the environmental impacts of steam power stations. One way is to use cleaner fuels, such as natural gas or renewable energy sources. Another way is to improve the efficiency of steam power stations. This can be done by using newer technologies, such as combined cycle power plants.
Steam power stations are a major source of electricity generation, but they also have a number of environmental impacts. It is important to weigh the benefits and drawbacks of steam power stations when considering their use.
The steam power plant should be placed near the coal mines so that the transport cost of fuel is at the lowest. However, if such a plant is to be established at a place where coal is not available, you need to make sure the fuel station is nearby.
Nature of land and its price:
The chosen site should have a high bearing capability of at least 10 N/sq mm to withstand the dead weight of the plant. It would lessen the cost of the base of the plant.
Availability of water:
The station must be positioned near a river bank or canal for constant water supply. The steam power plant utilizes water as a working solution throughout the year, which is regularly evaporated and condensed. It also wants about 2% of the steam produced as makeup water due to its loss.
Transportation facilities:
The station must be well attached to important transport routes eg Rail or Road. A new steam power plant often needs the transportation of material and machinery. Therefore, sufficient transportation facilities must exist i.e. the plant should be well attached to other parts of the land by rail, or road. etc.
Cost & type of land:
The land must have a great bearing capacity for heavy machinery and yet be affordable enough to purchase. The steam power plant should be located at a point where the property is cheap and further expansion if needed, is possible. Furthermore, the carriage capacity of the area should be enough so that heavy machinery could be installed.
Distance from populated areas:
The station must be established as far away from populated areas as possible due to air contamination.
Nearness to load centers:
In order to decrease the transmission cost, the plant should be placed near load centers. The location of the factory at the center of loads lessens the cost of transmission channels and the losses occurring in it.
Advantages and disadvantages of steam power plants
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Low Initial Cost: Economical setup compared to other power plants. | Low Efficiency: Overall efficiency is around 29% to 41%. |
| Less Land Required: Can be installed in smaller areas compared to hydroelectric plants. | Environmental Impact: Air pollution from fossil fuels contributes to climate change. |
| Fuel Flexibility: Can use coal, natural gas, oil, or biomass. | High Running Costs: Fuel and maintenance costs are high. |
| Reliable Power Source: Can generate electricity on a large or small scale. | Water Requirements: Needs a large water source. |
| Easy Installation: Can be set up near fuel and water supplies. | Noise Pollution: Can be noisy during operation. |
The Efficiency of Steam Power Plants
The overall efficiency of the steam power station is very average (about 29%) mainly due to two reasons. First, a large amount of heat is lost in the condenser and secondly, heat losses happen at different stages of the plant. The heat loss in the condenser cannot be withdrawn. It is because heat energy cannot be transformed into mechanical energy without temperature difference.
The greater the temperature variation, the greater the heat energy transformed into mechanical energy. This requires the steam in the condenser at the most moderate temperature. But we know that the higher the temperature difference, the greater is the value of heat loss. This demonstrates the average efficiency of such plants.
Main Component of Steam Power Plants
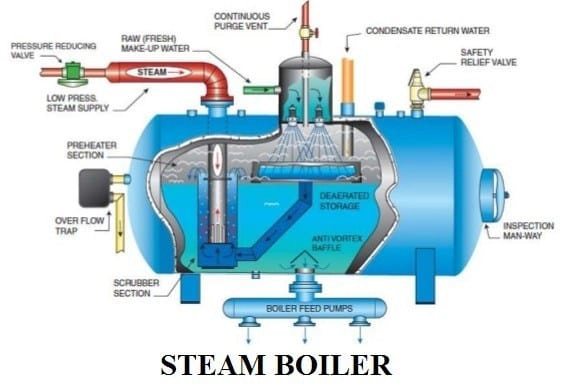
The boiler has the capacity to convert water into steam. The process of change of water to vapor is produced by heating the water in the tubes with energy from burning fuel. The combustion process is carried out continuously in the combustion room with fuel and airflow from the surface.
Thermodyne Engineering Systems is a Top Boiler Manufacturer in India
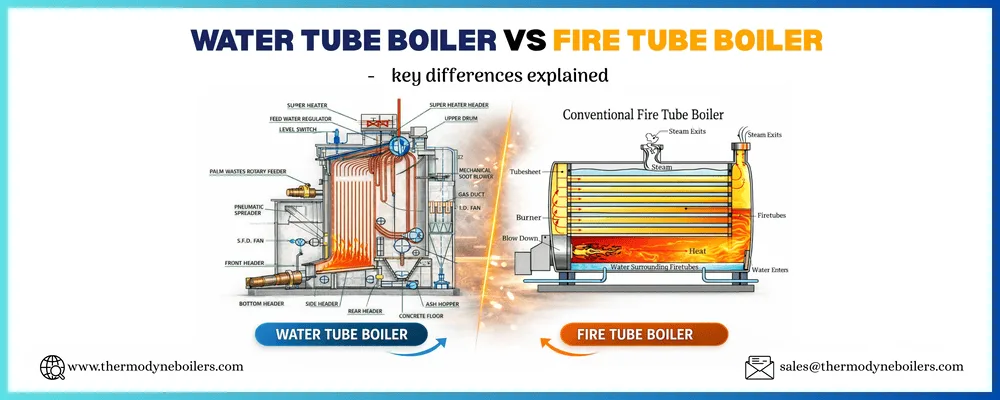
The resulting steam is superheated fumes which have high temperature and high pressure. The size of steam production depends on the surface area of heat transfer, flow rate, and the heat of combustion is applied. A boiler system consisting of water-filled pipes is called a water tube boiler.
Steam Turbine
The steam turbine works to change the heat energy carried in the steam into rotary motion. Steam with high load and temperature were conducted to push turbine blades installed on the shaft, so the shaft turns. Due to complete work on the turbine, the pressure and heat of steam coming into the turbine down to drenched vapor.
This steam then proceeds to the condenser, while the whirling power is used to turn a generator. Today nearly all of the steam turbine is a kind of condensing turbine.
Condenser
Condensers are tools to convert steam into water. The changes are made by the steam flow into a room holding tubes. Steam runs outside tubes, while the cooling water flows inside the tubes. This is called the surface condenser. It is usually for coolant use of seawater.
Heat transferal rate depends on the movement of cooling water, sanitation devices, and the temperature variation between the steam and cooling water. The method of change into water vapor happens at saturated weight and temperature. In this case, the condenser is beneath the vacuum.
Because the cooling water temperature is equal to the external temperature, the highest temperature condensate water near the outdoor air temperature. If the rate of heat transfer is suspended, it will affect the pressure and temperature.
Generator
The main idea of the activities at a plant is electricity. The electrical energy is produced by the generator. Function generator converts mechanical force into electrical energy in the form of a circle with the origin of magnetic induction.
The generator consists of a stator and rotor. The stator consists of the casing which holds coils and a rotor magnetic field station consists of a core comprising a coil.
Alternator
The steam turbine copulates to an alternators. When the turbine turns the alternator, electrical energy is produced. This generated electrical voltage is then walked up with the help of a transformer and then transferred where it is to be employed.
The working system of the Steam Power Plant
The working fluid cycle of the steam power plant is a final cycle, which uses the same fluid regularly. First, the water is loaded into the boiler to fill the whole surface area of heat transfer.
In the boiler, water is warmed by the hot gases of combustion fuel with air so that it gets transformed into the vapor phase. Steam generated by the boiler with pressure and temperature is guided to do work on the turbine to provide mechanical power in the order of rotation.
The former steam out of the turbine and then moved into the condenser to be frozen with cooling water that converted to water. Condensate water is then utilized again as boiler-feed water. Thus the cycle continues on and repeats.
The rotation of the turbine is utilized to turn a generator that is linked directly to the turbine. So when the turbine revolves, the generator output terminals produce electricity. Although the working fluid series is a closed cycle, the amount of water in the cycle would decline. The loss is due to the leakage of water either deliberately or accidentally.
Thermodyne Boilers is an Industrial Boiler Manufacturer in India
Steam Power Plant : Components, Application, and Working Mechanism FAQ
A steam power plant is a type of power plant in which heat energy is converted into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then used to turn a turbine, which generates electricity.
A steam power plant works by using a boiler to heat water until it turns into steam. The steam is then used to turn a turbine, which is connected to a generator. The generator converts the mechanical energy from the turbine into electrical energy. The steam is then condensed back into water and returned to the boiler to be heated again. This process is called the Rankine cycle.
There are two main types of steam power plants:
Conventional steam power plants: These plants use fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, or natural gas, to heat water and create steam.
Nuclear steam power plants: These plants use nuclear fission to heat water and create steam.
There are also a number of other types of steam power plants, including:
Geothermal steam power plants: These plants use geothermal energy to heat water and create steam.
Solar thermal power plants: These plants use solar energy to heat water and create steam.
Waste heat steam power plants: These plants use waste heat from other industrial processes to heat water and create steam.
Steam power plants have a number of advantages, including:
They are a reliable source of electricity.
They are relatively inexpensive to build and operate.
They can be used to generate electricity on a large or small scale.
They emit greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane. These gases contribute to climate change.
They require a large amount of water. This can be a problem in areas where water is scarce.
They can be noisy and can produce air pollution.
They emit greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane. These gases contribute to climate change.
They require a large amount of water. This can be a problem in areas where water is scarce.
They can be noisy and can produce air pollution.
Steam power plants emit a number of pollutants into the atmosphere, including:
Carbon dioxide
Methane
Sulfur dioxide
Nitrogen oxides
Particulate matter
These pollutants can contribute to a number of environmental problems, including:
Climate change
Acid rain
Smog
Respiratory problems
Cancer
The future of steam power plants is uncertain. On the one hand, steam power plants are a reliable and efficient way to generate electricity. On the other hand, steam power plants emit greenhouse gases and other pollutants that contribute to environmental problems.
It is likely that steam power plants will continue to be used in the future, but they will likely be used in conjunction with other forms of renewable energy, such as solar and wind power.
Some of the challenges facing steam power plants include:
The need to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases and other pollutants.
The need to find new and more efficient ways to generate steam.
The need to address the issue of water scarcity.
Some of the solutions to the challenges facing steam power plants include:
Using more efficient boilers and turbines.
Capturing and storing carbon dioxide emissions.
Using renewable energy sources to generate steam.
Developing new technologies to reduce water consumption
Some of the benefits of using steam power plants include:
They are a reliable source of electricity.
They are relatively inexpensive to build and operate.
They can be used to generate electricity on a large or small scale.
Some of the drawbacks of using steam power plants include:
They emit greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane. These gases contribute to climate change.
They require a large amount of water. This can be a problem in areas where water is scarce.
They can be noisy and can produce air pollution
There are two main ways to generate steam in a steam power plant:
Direct firing: In direct firing, the fuel is burned directly in the boiler. This is the most common way to generate steam in a steam power plant.
Indirect firing: In indirect firing, the fuel is burned outside of the boiler and the heat is transferred to the boiler using a heat exchanger. This method is less common than direct firing, but it can be used to generate steam with lower emissions.
There are two main types of turbines used in steam power plants:
Piston turbines: Piston turbines use the force of steam to move pistons. This type of turbine is not very efficient, but it is relatively inexpensive to build.
Turbines: Turbines use the force of steam to turn a shaft. This type of turbine is more efficient than a piston turbine, but it is also more expensive to build.
There are two main types of generators used in steam power plants:
Synchronous generators: Synchronous generators use the force of steam to turn a magnet. This type of generator is more efficient than an asynchronous generator, but it is also more expensive to build.
Asynchronous generators: Asynchronous generators use the force of steam to turn a coil of wire. This type of generator is less efficient than a synchronous generator, but it is also less expensive to build.
Fire-tube boilers: Fire-tube boilers have a series of tubes that are heated by fire. This type of boiler is the most common type of boilers used in steam power plants.
Water-tube boilers: Water-tube boilers have a series of tubes that are filled with water. The water is heated by fire and turns into steam. This type of boiler is more efficient than a fire-tube boiler, but it is also more expensive to build.
There are two main types of condensers used in steam power plants:
Water-cooled condensers: Water-cooled condensers use water to cool the steam. This type of condenser is the most common type of condenser used in steam power plants.
Air-cooled condensers: Air-cooled condensers use air to cool the steam. This type of condenser is less common than a water-cooled condenser, but it can be used in areas where water is scarce
Natural draft cooling towers: Natural draft cooling towers use the natural flow of air to cool the steam. This type of cooling tower is the most common type of cooling tower used in steam power plants.
Induced draft cooling towers: Induced draft cooling towers use fans to draw air through the cooling tower. This type of cooling tower is less common than a natural draft cooling tower, but it can be used in areas where the natural flow of air is not strong enough
The most common types of fuel used in steam power plants are:
Coal: Coal is the most common type of fuel used in steam power plants. It is relatively inexpensive and abundant.
Oil: Oil is more expensive than coal, but it is cleaner burning.
Natural gas: Natural gas is the cleanest burning type of fuel used in steam power plants. It is also relatively inexpensive.
If you are still looking for more information regarding steam power station/plant then check out our Thermal Power Plant related Post and Boiler terminology for component details.
Learn About Thermodyne Engineering Systems
Boiler Resources
Boiler Losses That Eat Away Your Profits
Dissolved Gases in Feed Water and Its Effect
Pressure Reduction System
How to Minimize the Blowdown Losses
Awards and Recognition