Principle Fluidized Bed Combustion Boiler (FBC Boiler)
- A fluidized bed is created when a gas is passed through a bed of solid particles at a high enough velocity. The gas flow causes the particles to become suspended in the gas stream, like a fluid.
- This allows for better mixing of the fuel and air, which leads to more efficient combustion. The high temperature of the fluidized bed also helps to break down pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
Fluidized bed combustion is a versatile technology that can be used to burn a variety of fuels, including coal, biomass, and waste. It is a more efficient and environmentally friendly way to produce heat and power than traditional combustion methods.
“Fluidized bed combustion(FBC) is a combustion technology used to burn solid fuels.“In fluidized bed combustion (FBC), solid fuels are burned in a bed of suspended particles, creating a highly efficient and environmentally friendly combustion process. The fluidized bed allows for better fuel mixing, higher combustion rates, and lower emissions compared to traditional combustion methods.
A bed of solid particles is said to be fluidized when the pressurized fluid (liquid or gas) is passed through the medium and causes the solid particles to behave like a fluid under certain conditions. When a pressurized fluid (liquid or gas) flows through a bed of solid particles, they become suspended and exhibit fluid-like behavior, forming a fluidized bed. This fluidization phenomenon enhances heat transfer and promotes efficient reactions in various industrial processes such as combustion and chemical reactions.
Fluidization causes the transformation of the state of solid particles from static to dynamic.
Benefits of Fluidized Bed Combustion (FBC) in Boiler Systems
Fluidized Bed Combustion (FBC) is a popular boiler technology in India and Asia due to its many advantages.
- Enhanced Combustion Efficiency: FBC boilers mix fuel and air more effectively than conventional boilers, resulting in higher thermal efficiency and improved energy output.
- Reduced Emissions: FBC boilers produce lower emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and particulate matter. This is beneficial for air quality and compliance with environmental regulations.
- Fuel Flexibility: FBC boilers can burn a wide range of fuels, including coal, biomass, petcoke, and even waste materials. This gives industries the flexibility to adapt to changing fuel availability and cost fluctuations.
- Lower Operational Costs: Due to improved combustion efficiency, FBC boilers require less fuel for the same heat output. This reduces fuel costs and overall operational costs.
Diagram OF Fluidized Bed Combustion Boiler (FBC Boiler)
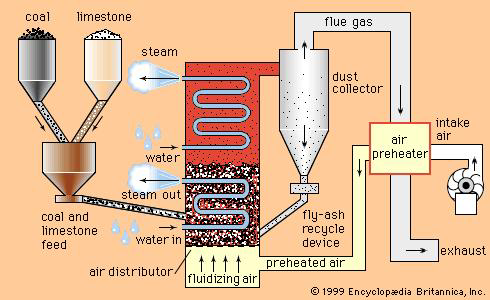
Source of Fluidized Bed Combustion Image: Britannica
Fluidized Bed Combustion is the ignition of a solid fuel under the conditions mentioned above.
We, At Thermodyne, Boiler Manufacture in India, design and manufacture Boilers with
Type OF Fluidized Bed Combustion (FBC Boiler)
- Bubbling Fluidized Bed Combustion (BFBC)
- Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion (CFBC).
Bubbling FBC is used for Fuels with lower heating values such as Rice Husk. Bubbling FBC is a commonly employed combustion method for fuels with lower heating values, such as Rice Husk, due to its ability to efficiently burn and utilize such biomass materials. Under such sort, the main factors leading to fluidization are as follows: Solid Fuel Particle Size Air Fuel Mixture
Fluidized Bed Combustion takes place when the forced draught fan supplies air to the Furnace of the Boiler. In the furnace, and is (used for the Bubbling phenomenon) placed on the Bed and is heated before fluidization, the air enters the bed from the nozzles fitted on the Furnace Bed. And above the nozzles; the sand opposes the upward motion of the air.
But at sufficient velocities, when the pressure applied by the air becomes equal to the weight of the sand, fluidization of the sand occurs.
Now the fuel supplied by the fuel conveyor is fed to the preheated bubbling sand and gets combusted away. This phenomenon also ensures the complete combustion of the Fuel.
The heat released during combustion heats up the surrounding boiler tubes and generates steam. The major advantages of Bubbling Fluidized Bed Combustion are enhanced thermal efficiency and easy ash removal.
Another type is the Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion; it is applied to fuels with higher heating values such as Petcoke.
In this, the unburned fuel is fed again to the furnace with the help of a Forced Draught fan and ducts, ensuring enhanced combustion and higher heating and providing excellent fuel flexibility.
Also, the fluidizing velocity of Air in CFBC is comparatively higher than that of BFBC. One of the major drawbacks is the power consumption.
The motors installed in the Forced Draught Fan consume more power than the one installed in the same capacity Boiler’s ( wood/coal fired) Forced Draught Fan, because of elevated levels of draught requirement to create fluidization.
What is a fluidized bed boiler?
A fluidized bed boiler is a type of boiler where solid particles, like coal or biomaterials, are suspended in a stream of air or gas, forming a “fluidized” bed of particles. The bed behaves like a fluid, hence the name “fluidized bed.” This process improves combustion efficiency and heat transfer because the particles are constantly in motion and have a large surface area, allowing for better mixing of fuel and oxygen.
Fluidized bed boilers are commonly used in power plants and industrial processes that require efficient combustion of solid fuels. They offer several advantages, including flexibility in fuel choices, low emissions of pollutants, and the ability to burn low-quality fuels. The fluidized bed also helps in controlling the combustion temperature, which can be useful in processes requiring specific temperature ranges.
What is a fluidized bed boiler and mechanism
A fluidized bed boiler is an intriguing combustion system that suspends solid particles in an upward flow of gas or air. The process of “fluidization” characterizes the behavior of solid particles, which resemble the characteristics of a fluid due to the upward velocity induced by the gas stream. This results in a highly efficient combustion process, facilitating a superior combination of fuel and air.
The fluidized bed combustion mechanism is composed of distinct stages, including the “Incendiary Ballet,” wherein fuel particles are mixed with the gas stream to culminate in balletic combustion. Following this, the “Thermal Waltz” stage follows, in which heat produced by the combustion process is transferred to a network of water tubes within the fluidized bed. This transforms water into steam, which is suitable for powering various applications, including generating electricity. Finally, the “Ash Pas de Deux” stage involves the expulsion of ash, which is an essential step in ensuring the continued performance of the fluidized bed.
The symphony of a fluidized bed boiler offers numerous advantages, including efficient combustion, minimal pollutant emissions, and fuel flexibility. This mechanism can accommodate a wide range of fuels, from coal to biomass, and even allows for waste materials to be used, making it highly versatile. Additionally, the choreography of fluidized bed combustion reduces emissions of harmful pollutants, making it an eco-conscious solution for energy production.
Overall, fluidized bed boilers are an impressive and sustainable option for energy production, elevating fuel efficiency and curbing the environmental impact of energy production. Their unique combustion mechanism enhances energy ingenuity and fosters environmental stewardship.
Also Read: Thermic Fluid Heaters
FAQ
Fluidized bed combustion boiler (FBC) is a combustion technology used to burn solid fuels. In its most basic form, fuel particles are suspended in a hot, bubbling fluidity bed of ash and other particulate materials through which jets of air are blown to provide the oxygen required for combustion or gasification. The resultant fast and intimate mixing of gas and solids promotes rapid heat transfer and chemical reactions within the bed. FBC plants are capable of burning a variety of low-grade solid fuels, including most types of coal, coal waste, and woody biomass, at high efficiency and without the necessity for expensive fuel preparation (e.g., pulverizing).
FBC offers a number of benefits over traditional combustion technologies, including:
Increased efficiency: FBC plants can achieve efficiencies of up to 90%, compared to 30-40% for traditional coal-fired power plants.
Reduced emissions: FBC plants can significantly reduce emissions of pollutants such as NOx, SO2 and particulate matter.
Flexibility: FBC plants can burn a variety of solid fuels, including low-grade coal, biomass and waste.
Cost savings: FBC plants can save money on fuel costs and operating expenses.
Complexity: FBC plants are more complex to operate and maintain than traditional coal-fired power plants.
Corrosion: FBC plants are more prone to corrosion than traditional coal-fired power plants.
Power generation: FBC is used to generate electricity in power plants.
Industrial heating: FBC is used to heat industrial processes.
Waste treatment: FBC is used to treat waste materials, such as sewage sludge and biomass.
FBC boiler is a promising technology with the potential to reduce emissions and improve efficiency in a variety of applications. The future of FBC looks bright, as more and more countries and companies adopt this technology to help meet their environmental and energy goals.
There are two main types of fluidized bed combustion boiler
Atmospheric fluidized bed combustion (AFBC): AFBC plants operate at atmospheric pressure.
Pressurized fluidized bed combustion (PFBC): PFBC plants operate at elevated pressure.
Lower capital costs than PFBC plants.
Simpler design and operation than PFBC plants.
More flexible fuel options than PFBC plants.
Higher efficiency than AFBC plants.
Lower emissions of NOx and SO2 than AFBC plants.
Less prone to corrosion than AFBC plants.
Higher capital costs than AFBC plants.
More complex design and operation than AFBC plants.
Fewer fuel options than AFBC plants.





