- Rice is a common food source in various cuisines and cultures.
- Rice is a staple food for a significant portion of the world population.
- In India, where agriculture is a primary occupation, rice-based industries are in high demand.
- Starting a rice mill business can be profitable.
“Rice is a primary food source in many places around the world, including India where agriculture plays a major role in the economy.”
Process of Rice Mill Plant
Starting a rice mill plant business is a significant venture, and having a reliable boiler is crucial for the success of your operations. In the context of your industry, a boiler plays a pivotal role in the rice milling process, contributing to the overall efficiency and quality of the final product.
“Rice is a primary food source in many places around the world, including India where agriculture plays a major role in the economy.”
Importance of a Boiler in a Rice Mill Plant
Steam Generation:
- Boilers are essential for generating steam, a key element in the rice milling process.
- Steam is used for parboiling, drying, and polishing the rice, ensuring a high-quality end product.
Energy Source:
- Boilers serve as a primary source of energy for various machinery in the rice mill.
- They provide the necessary heat for drying paddy, maintaining the ideal moisture content for milling.
Parboiling Process:
- Parboiling is a crucial step in rice milling to enhance the nutritional value and improve the milling quality.
- Boilers facilitate the parboiling process by supplying steam to steam jackets or vessels.
Drying Operation:
- Boilers are indispensable for drying the harvested paddy before milling.
- Efficient drying ensures uniform milling and prevents mold or bacterial growth.
Steam for Cleaning and Polishing:
- Steam generated by boilers is utilized for cleaning and polishing rice grains.
- This step enhances the appearance and marketability of the final rice product.
Economic Viability:
- Investing in a high-quality boiler ensures a reliable and continuous energy supply, contributing to the economic viability of the rice mill.
Environmental Considerations:
- Modern boilers designed with eco-friendly features contribute to sustainable and environmentally responsible operations.
Choosing the Right Boiler for Your Rice Mill
Capacity and Efficiency:
- Assess the processing capacity of your rice mill to determine the appropriate boiler size.
- Opt for energy-efficient boilers to reduce operational costs.
Fuel Type:
- Consider the availability and cost of different fuel options (such as biomass, coal, or gas) when selecting a boiler.
Technology and Automation:
- Explore boilers with advanced control systems for improved efficiency and ease of operation.
- Automation features contribute to better process control.
Compliance and Safety:
- Ensure that the chosen boiler complies with safety regulations and industry standards.
- Regular maintenance is essential to guarantee safe and reliable operation.
Process of Rice Mill Plant
The rice milling process involves several steps to transform paddy rice into polished rice that is ready for consumption. Here is a step-by-step explanation of the process along with the names of some common instruments used
Process of Rice Mill Plant
The rice milling process involves several steps to transform paddy rice into polished rice that is ready for consumption. Here is a step-by-step explanation of the process along with the names of some common instruments used
Cleaning
Winnowing
Winnowing is a method to separate impurities like straw, dust, and stones from rice. It’s done by letting the wind or a fan blow over the rice on a tray. Lighter rice grains are carried away by the wind, while heavier impurities stay behind.

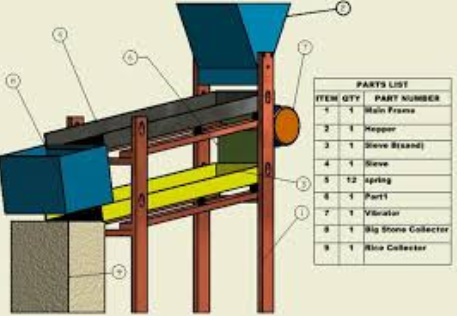
Destoner
A destoner is a machine that removes heavy stones from rice. It does this by shaking the rice, causing the stones to sink to the bottom, while the rice remains on top. This ensures that the rice is free from stones, making it safe to eat.
Hulling
Hulling is a process where a machine called a huller is used to take off the outer husk layer from paddy grains, which are essentially rice with their protective covering still on. When you remove this outer husk, you get what we call brown rice.

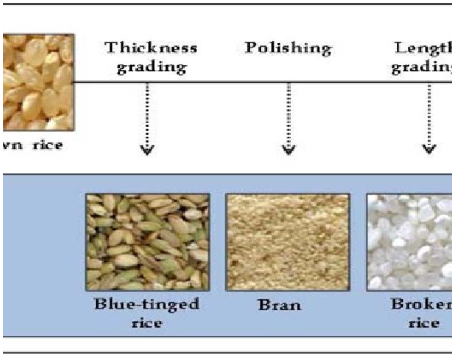
Whitening
After hulling, you have brown rice, but it’s not the white rice you typically see. To make it white, a machine known as a whitener comes into play. This machine has rollers with a rough surface that rub against the brown rice. This rubbing action gently removes the bran layer, which is the outer covering of brown rice. When this bran is removed, what’s left is the familiar white rice we often eat. So, whitening turns brown rice into white rice by polishing it.
Polishing
Polishing is the step where rice grains are given extra attention to make them look and feel better. A machine called a polisher is used for this. It’s like giving the rice grains a nice, smooth finish. This doesn’t change their taste or nutrition; it just makes them more attractive and pleasant to eat.

Grading and Sorting
After polishing, rice goes through two important processes to ensure it’s of high quality.
Grading
Grading is like organising the rice grains by size. A machine called a grader is used for this purpose. It separates the rice into different categories based on their size. This is important because rice grains of the same size cook evenly and look nice when served.


Color Sorter
To make sure every grain is perfect, another machine called a color sorter is used. This machine uses special sensors to look at each grain closely. If it spots any rice grain that looks discoloured or has some defect, it removes it from the batch. This way, only the best and most perfect rice grains make it to your plate. It’s like having an extra set of eyes to check every grain for you.
Packaging
Packaging Machine: A packaging machine is a device used in the rice processing industry to efficiently fill and seal rice in bags or containers. It automates the process of packaging rice, ensuring that it is securely enclosed in packaging materials for distribution and sale.


Storage
Silos: Silos are substantial storage containers specifically designed for the purpose of storing processed rice. They are typically large, cylindrical structures made of durable materials such as steel or concrete. Silos provide a controlled environment for storing rice, protecting it from external factors like moisture, pests, and contamination. This ensures the quality and integrity of the rice until it is ready for further processing or distribution.
Quality Control
A moisture meter is a device that helps us measure how much water or moisture is present in rice. You can think of it as a tool that tells us if the rice is too dry or too wet. This is important because the moisture level in rice affects its quality and how well it cooks.
Rice Quality Analyzer is like a machine that examines different things about the rice to see if it’s good or not. It checks various factors that determine if the rice is of high quality. These factors can include things like the size and shape of the rice grains, any impurities or foreign materials in the rice, and even the colour and smell of the rice.
Transportation
Conveyor Belts: These are like moving roads that help rice move from one processing stage to another. They keep the rice flowing smoothly through different parts of the production process.
Buckets: These are used in elevators to lift rice vertically from one level to another. They act like containers that carry rice upward, making it easier to transport rice to different heights within a rice processing facility.
Waste Management
A Paddy Separator is a machine that separates any leftover paddy (unhusked rice) from the rice we want to eat. It helps ensure that we get clean, ready-to-cook rice without any unwanted parts.
Water Management
Water Pump: This device is used to supply water at certain stages of the rice milling process. It’s like a machine that pushes water where it’s needed.
Water Tank: A water tank stores water for use in the rice milling process. Think of it as a big container that holds water until it’s needed to help with different parts of making rice.
Energy Sources
Electric Motors: These power various machines used in the rice processing. Think of them as the engines that make the machines run.
Diesel Generators: These provide backup power if there’s an electricity outage. They act like backup engines to keep the machines running even when there’s no electricity.
Automation
Electric Motors: These power various machines used in the rice processing. Think of them as the engines that make the machines run.
Diesel Generators: These provide backup power if there’s an electricity outage. They act like backup engines to keep the machines running even when there’s no electricity.
The rice milling process can vary in complexity depending on the desired end product and the scale of the mill. These are the essential steps and instruments used in a typical rice milling process.
Parboiling in the Rice Mill Process
Parboiling is a crucial step in the rice milling process, particularly in India and Asia, where rice is a staple food. This technique not only enhances the nutritional value of rice but also improves its texture and cooking properties. In this blog, we will delve into the parboiling process in rice mills, its significance, and how it contributes to the quality of rice.
What is Parboiling?
Parboiling is a partial cooking process that involves soaking, steaming, and drying rice paddy before it undergoes the milling process. The term “parboil” comes from “partial boiling.” It is an essential step in rice production, as it alters the rice grain’s composition and structure.
The Parboiling Process
Soaking: The process begins with soaking the rice paddy in water. This step allows the moisture to penetrate the grain and initiate gelatinization, where the starches in the rice become partially cooked.
Steaming: After soaking, the rice is steamed. During steaming, the rice paddy is exposed to high-temperature steam, which completes the gelatinization process. This step ensures that the rice becomes more transparent and firmer.
Drying: Once steamed, the rice is dried to reduce its moisture content. Proper drying is critical to prevent mould growth and to store the rice for an extended period.
These are the Model used in Rice mill industry all the necessary details below in table.
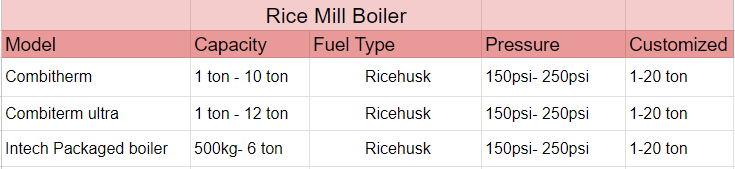
Ricemill Boiler Calculator

This is approximate calculation for exact calculation you can contact our sale person.
Ricemill Boiler Calculator Manual
To determine the boiler requirements for your paddy dryer, follow these steps:
Input the capacity of your paddy dryer in tons. For example, if you a 24-ton paddy dryer, enter 24.
The calculator will provide you with the recommended boiler capacity in tons. For a 24-ton paddy dryer, the recommended boiler capacity is 2 tons.
Using the Calculator:
Our Rice Mill Boiler Calculator is a user-friendly tool designed to simplify the process of determining your boiler needs. Simply input your paddy dryer capacity, and it will provide you with the required boiler capacity.
Paddy Dryer Capacity Reference:
24 Ton
32 Ton
40 Ton
50 Ton
This is approximate calculation for exact calculation you can contact our sale person.
For free Consultation
please call us at 9990226006
The flyer of Rice mill boilers
The video for rice mill industry
Unit 1: THERMODYNE ENGINEERING SYSTEMS,
A-7/110 SSGT Road Industrial Area,
Ghaziabad, UP, INDIA.
Unit 2: E-11 South East Zone MIA, Alwar – 301030, Rajasthan (India).
Phone : +91 – 120 – 4562332,
+91-1204110482
+91 9990226006
info@thermodyneboilers.com
sales@thermodyneboilers.com
sales1@thermodyneboilers.com
How to Start Rice Mill Plant Business FAQ
- Cleaning: The paddy rice is cleaned to remove any dirt, dust, or other debris.
- Dehusking: The husk is removed from the paddy rice.
- Whitening: The bran layers are removed from the rice kernel.
- Polishing: The rice kernel is polished to give it a smooth, white appearance.
- Grading: The rice is graded into different categories based on its quality and size.
- Conduct a market study to determine the demand for rice in your area.
- Choose a suitable location for your mill.
- Purchase the necessary equipment and machinery.
- Hire qualified staff to operate the mill.
- Obtain the necessary permits and licenses.
- Cleaning: The paddy rice is cleaned to remove any dirt, dust, or other debris.
- Dehusking: The husk is removed from the paddy rice.
- Whitening: The bran layers are removed from the rice kernel.
- Polishing: The rice kernel is polished to give it a smooth, white appearance.
- Grading: The rice is graded into different categories based on its quality and size.
- Packaging: The rice is packaged into bags or sacks for sale.
- Paddy cleaners
- Dehuskers
- Whiteners
- Polishers
- Graders






