Plywood
Plywood
Plywood
Plywood
Veneer Drying
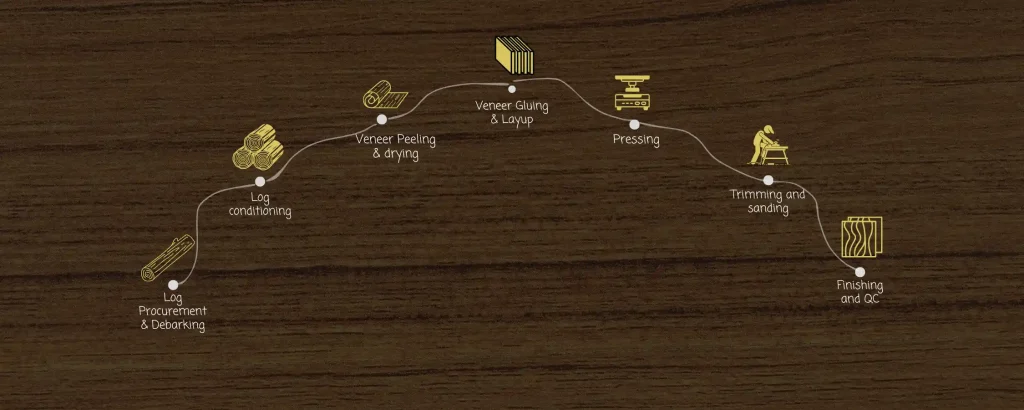
- After the veneer is peeled from logs, it contains high moisture content. Dryers use steam generated by boilers to remove excess moisture and reduce the moisture content to optimal levels.
- The steam from the boiler is used to heat the drying chambers or direct steam drying units, ensuring a uniform drying process, which is critical for producing high-quality plywood.
Log Conditioning
- Before peeling, logs are either soaked in hot water or exposed to steam to soften the wood fibres, making it easier to peel thin veneer layers.
- Boilers provide the steam necessary for heating the water or for direct steam treatment. This softens the logs, reducing cracking and improving veneer quality.
Pressing
- In the hot pressing process, multiple veneer layers are bonded together with adhesive, with heat and pressure applied to cure the adhesive and set the layers.
- Boilers supply the steam required to heat the hydraulic presses that bond the veneer layers. The controlled steam pressure ensures even heating, critical for strong adhesion.
Resin/Adhesive Curing
- The resin or adhesive used to bond veneer layers needs to be cured under heat to form a strong bond.
- The steam generated by boilers is often used in the curing process, ensuring that adhesives are set properly without over- or under-curing, which could compromise product quality.
Heating of Industrial Equipment
- Various machines, such as lamination equipment and edge finishers, require heat to process plywood sheets and apply surface treatments.
- Boilers provide the steam or hot water necessary to maintain optimal equipment temperatures for consistent plywood processing.
Thermal Treatment
- Some plywood products undergo thermal treatment to improve durability, moisture resistance, or fire resistance.
- Boilers generate the steam or heat required to perform these thermal treatments, ensuring uniform application.
Plywood
Veneer Drying
- After the veneer is peeled from logs, it contains high moisture content. Dryers use steam generated by boilers to remove excess moisture and reduce the moisture content to optimal levels.
- The steam from the boiler is used to heat the drying chambers or direct steam drying units, ensuring a uniform drying process, which is critical for producing high-quality plywood.
Log Conditioning
- Before peeling, logs are either soaked in hot water or exposed to steam to soften the wood fibres, making it easier to peel thin veneer layers.
- Boilers provide the steam necessary for heating the water or for direct steam treatment. This softens the logs, reducing cracking and improving veneer quality.
Pressing
- In the hot pressing process, multiple veneer layers are bonded together with adhesive, with heat and pressure applied to cure the adhesive and set the layers.
- Boilers supply the steam required to heat the hydraulic presses that bond the veneer layers. The controlled steam pressure ensures even heating, critical for strong adhesion.
Resin/Adhesive
Curing
Curing
- The resin or adhesive used to bond veneer layers needs to be cured under heat to form a strong bond.
- The steam generated by boilers is often used in the curing process, ensuring that adhesives are set properly without over- or under-curing, which could compromise product quality.
Heating of Industrial
Equipment
Equipment
- Various machines, such as lamination equipment and edge finishers, require heat to process plywood sheets and apply surface treatments.
- Boilers provide the steam or hot water necessary to maintain optimal equipment temperatures for consistent plywood processing.
Thermal Treatment
- Some plywood products undergo thermal treatment to improve durability, moisture resistance, or fire resistance.
- Boilers generate the steam or heat required to perform these thermal treatments, ensuring uniform application.
