In addition to other contaminants, natural water or raw water that is directly sourced from resources has various gases dissolved in it. These gases are produced by atmospheric air. In terms of boiler feed water, we are primarily concerned with oxygen and carbon dioxide, but other gases still make up a modest portion. These gases have an effect on the lifespan and operation of the boiler. Oxygen causes corrosion, which eventually causes the system to fail. It also lowers the quality of the steam, uses more fuel, reduces efficiency, and causes steam leakage. which is undesirable for a boiler operation that runs smoothly.
Oxygen Pitting: A Major Cause of Boiler Corrosion
Oxygen pitting is a type of corrosion that occurs when oxygen dissolves in boiler water. The oxygen molecules react with the metal in the boiler, forming pits or holes. These pits can weaken the boiler and eventually lead to failure.
There are a number of factors that can contribute to oxygen pitting, including:
High temperatures: The higher the temperature of the boiler water, the more oxygen can dissolve in it.
Low pH: A low pH level makes the boiler water more acidic, which increases the risk of corrosion.
Improper water treatment: If the boiler water is not properly treated, it can contain impurities that can accelerate corrosion.
To prevent oxygen pitting, it is important to:
- Keep the boiler water temperature at a safe level.
- Monitor the pH level of the boiler water and keep it within the recommended range.
- Use a water treatment program that removes impurities from the boiler water.
By following these steps, you can help to prevent oxygen pitting and keep your boiler in good working condition.
Here are some additional tips for preventing oxygen pitting:
- Install a deaerator on your boiler. A deaerator removes dissolved oxygen from the boiler water, which helps to prevent corrosion.
- Use a chemical oxygen scavenger. A chemical oxygen scavenger reacts with dissolved oxygen in the boiler water, forming a harmless compound.
- Inspect your boiler regularly for signs of corrosion. If you see any pits or holes, have them repaired immediately. By following these tips, you can help to extend the life of your boiler and prevent costly repairs.
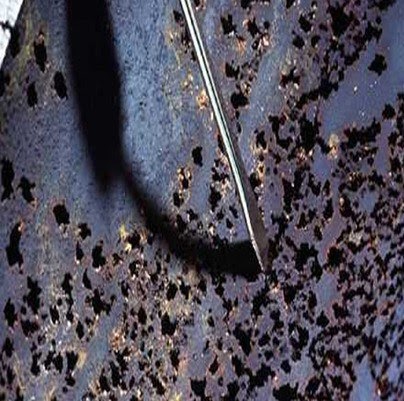


Below is a detailed description of how oxygen and carbon dioxide affect boiler performance.
Effect of oxygen
One of the most dangerous gases in water is oxygen; even a relatively small amount can seriously destroy the boiler system. It causes rust and corrosion known as oxygen pitting or oxygen attack when it reacts with iron-carbon steel. Oxygen is more corrosive at higher temperatures. This oxygen attack may be localized or contained to a specific area, which ultimately results in system failure or leakage.
Pits are small, localized corrosion spaces created by oxygen. Oxygen pits may quickly “drill” through metal surfaces, which causes metal to become worn down and fail. The iron surface dissolves as oxygen corrodes the boiler metal. In addition to weakening the metal site, this also introduces dissolved iron into the boiler. This dispersed iron can build up on boiler tubes, scorching them and leading to tube failure.
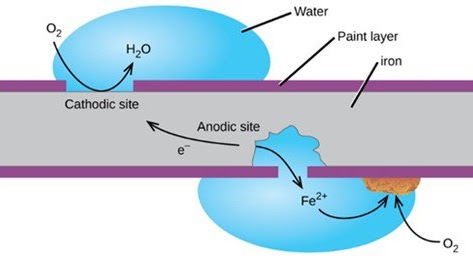
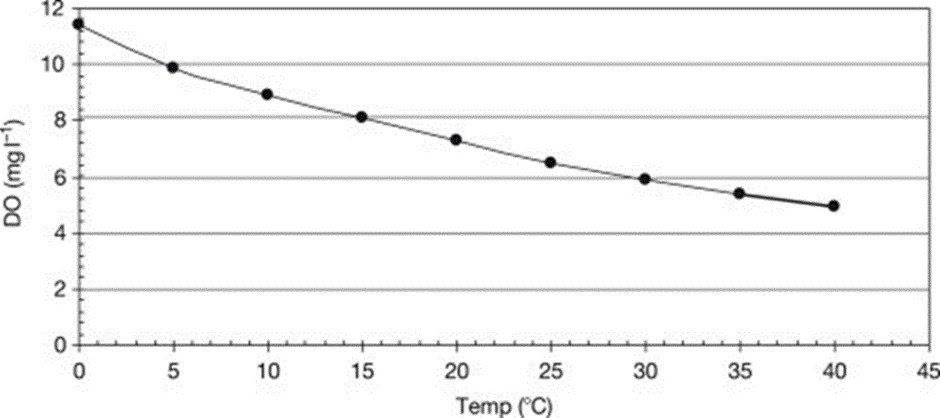
Temperature and pressure affect how soluble oxygen is in water; at constant pressure, solubility reduces as temperature rises, whereas at constant temperature, solubility rises with pressure.
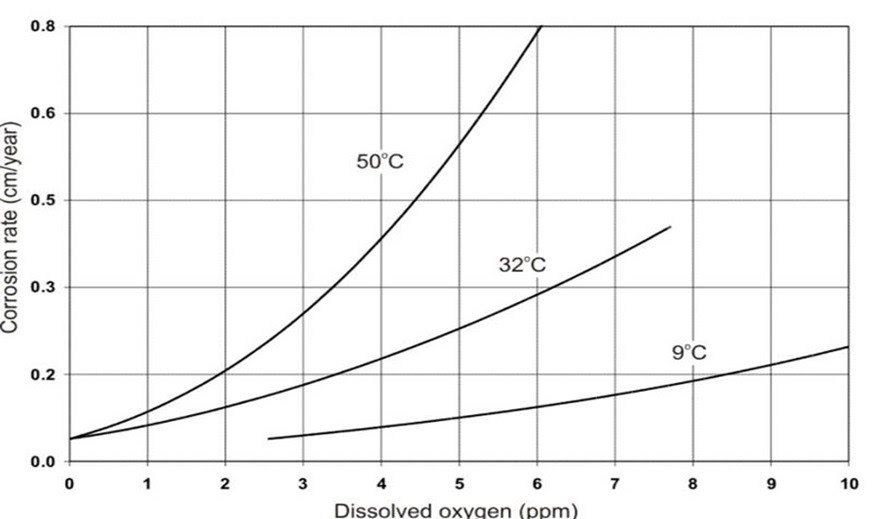
When temperatures are high, oxygen becomes more corrosive and breaks down metal more quickly than when temperatures are low. This accelerates the system’s breakdown.
Effect of Temperature on Corrosion
Effect of carbon dioxide:
Because the deaeration process removes the gases from the feed water, the make-up water after deaeration often has no CO2 content. It is the condensate that contains CO2 most frequently, therefore the condensate tank quite often experiences CO2 corrosion. The decomposition of carbonate and bicarbonate in condensate under boiler conditions is typically what causes the presence of the gas in condensate. Both oxygen and free carbon dioxide can be removed from the feed water by heating it in the feed tank and keeping it there while it is being delivered to the boiler.
We are Here to Help You!
Major Cause of Boiler Corrosion FAQ:
Yes, boilers can be dangerous if they are not properly maintained. Boilers can overheat, explode, or release toxic fumes.
The most common dangers associated with boilers include:
Explosion: A boiler explosion can cause serious injuries or death.
Overheating: Overheating can cause the boiler to rupture, releasing hot water or steam.
Toxic fumes: Boilers can release toxic fumes, such as carbon monoxide, if they are not properly vented.
To prevent boiler accidents, you should:
Have your boiler inspected and serviced by a qualified technician on a regular basis.
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for operation and maintenance.
Be aware of the signs of a potential problem, such as leaks, overheating, or smoke.
Do not operate a boiler if it is damaged or malfunctioning.
The signs of a boiler problem may include:
Leaks: If you see water or steam leaking from your boiler, turn it off and call a qualified technician.
Overheating: If your boiler is overheating, turn it off and let it cool down before using it again.
Smoke: If you see smoke coming from your boiler, turn it off and call a qualified technician.
Damage: If your boiler is damaged, do not use it. Call a qualified technician to repair it.
If you suspect a boiler problem, you should:
Turn off the boiler.
Ventilate the area.
Call a qualified technician.
The safety precautions you should take when working with boilers include:
Always wear safety glasses and gloves.
Be aware of the location of the shut-off valve.
Never operate a boiler if you are tired or under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Do not overload the boiler.
Do not use the boiler for anything other than its intended purpose.
The fire safety precautions you should take when working with boilers include:
Keep the area around the boiler clear of flammable materials.
Have a fire extinguisher on hand.
Know how to use the fire extinguisher.
**Be trained in fire safety.
The fire safety precautions you should take when working with boilers include:
Keep the area around the boiler clear of flammable materials.
Have a fire extinguisher on hand.
Know how to use the fire extinguisher.
**Be trained in fire safety.
The environmental safety precautions you should take when working with boilers include:
Dispose of boiler waste properly.
Ventilate the area to prevent carbon monoxide buildup.
**Be aware of the environmental regulations that apply to your boile
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
The American Boiler Manufacturers Association (ABM)
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
Your local fire department
**Your local boiler manufacturer






