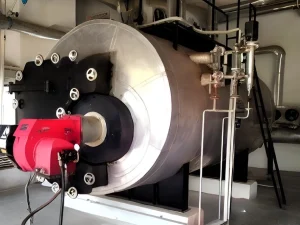
Oil Fired Boiler (Savemax) – Engineered for Superior Efficiency, Reliability & Industrial Performance

Oil Fired Boiler -Savemax
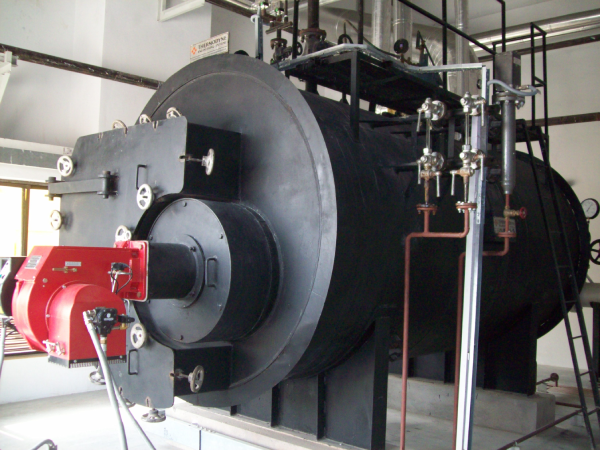
The Savemax is a three-pass, smoke-tube design, gas or oil fired boiler with an internal water-cooled furnace. This design ensures high efficiency and optimal performance, making it the ideal choice for various industrial applications.
Featuring a standard three-pass internal furnace smoke tube configuration with water enclosed reversal chamber. This design ensures enhanced heat transfer as the reversal chamber and the furnace are surrounded by water on all sides, making effective heat transfer of the flue gases to the water. The flue gases travel through the tubes in the 2nd and 3rd passes, delivering maximum heat to the water thereby producing steam efficiently.
1 TPH- 20 TPH
- Light oil
- Heavy oil
- PNG
- LPG
- Biogas
- Oil fired
- Gas fired
- Dual fuel fired (Oil cum gas)
- Pharmaceuticals
- Textiles
- Food processing
- Chemicals
- Rubber
- Dairy
- Beverages and others
Oil fired boiler related FAQ's -
An oil fired boiler is a type of industrial boiler that uses oil—such as light diesel oil, furnace oil, or heavy oil—as its primary fuel source to generate steam or hot water for various industrial processes
Oil fired boilers can use the following types of oil:
Light Diesel Oil (LDO)
Furnace Oil (FO)
Heavy Oil
These are the most common fuel oils used for industrial oil fired boilers
The oil fired boiler working process involves burning fuel oil in a combustion chamber. The heat produced transfers to water through a heat exchanger, generating steam or hot water for industrial use. Exhaust gases are safely expelled through the flue system.
Yes, oil fired steam boilers are available in both low and high-pressure configurations to meet industrial demands.
Key components include:
Burner (for oil combustion)
Combustion chamber
Heat exchanger
Water tubes or shell
Steam drum (for steam boilers)
Flue gas ducting and chimney
Control systems and safety devices
Oil fired boilers are widely used in industries such as food processing, chemical manufacturing, textile, pharmaceuticals, paper, and small-scale manufacturing where reliable steam or hot water is required.
High efficiency and rapid steam generation
Consistent and controllable heat output
Suitable for locations without access to natural gas
Compact design options for limited space industries
Lower emissions with modern burners and controls
Consider the following factors:
Required steam or hot water output (capacity)
Operating pressure
Fuel type and availability
Space constraints
Efficiency ratings
Budget and operational costs
Maintenance requirements
Common types include:
Scotch marine boiler
Locomotive boiler
Cornish boiler
Lancashire boiler
Vertical fire-tube boiler