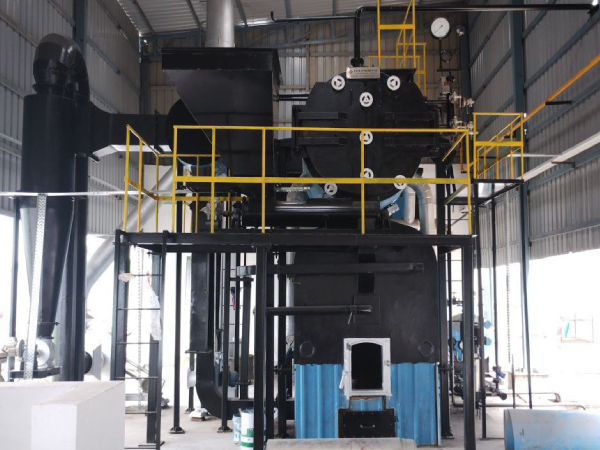
Rice Mill
Rice Mill
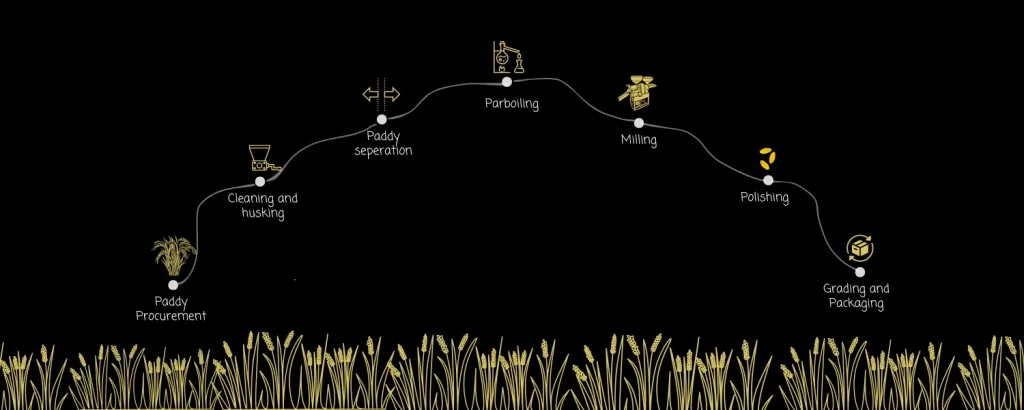
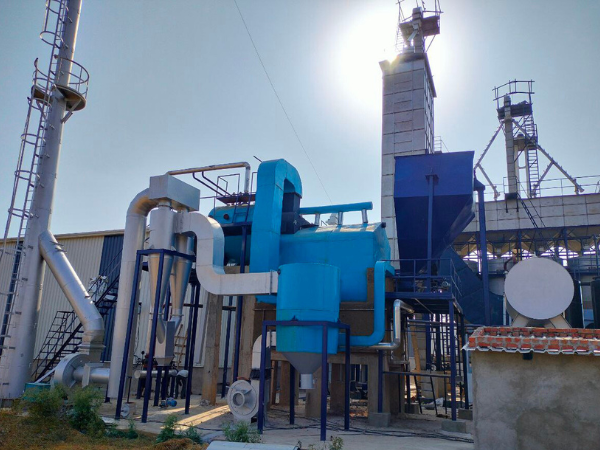
Rice Mill
Application of boiler in rice mill for Parboiling
Soaking
- The paddy is soaked in water to increase the moisture content of the grains to around 30-35%.
- The paddy is placed in large tanks filled with water. The soaking duration can vary from several hours to a couple of days, depending on the desired end quality.
- Warm water soaking is preferred to expedite the process and to ensure uniform moisture absorption.
Steaming
- To gelatinize the starch within the rice grains, making them harder and less prone to breakage during milling.
- The soaked paddy is exposed to steam in steam chambers or parboiling tanks.
- The steaming process typically lasts for 20-30 minutes, depending on the desired level of gelatinization.
- High pressure and temperature are maintained to ensure uniform steaming.
Drying
- To reduce the moisture content of the steamed paddy to around 14% for safe storage and milling.
- The drying can be done using sun drying, hot air dryers, or mechanical dryers.
- Initial rapid drying followed by slow drying to prevent cracking of the grains.
- Proper control is maintained to ensure even drying and to avoid damage to the rice grains.
Application of boiler in rice mill for Parboiling
Soaking
- The paddy is soaked in water to increase the moisture content of the grains to around 30-35%.
- The paddy is placed in large tanks filled with water. The soaking duration can vary from several hours to a couple of days, depending on the desired end quality.
- Warm water soaking is preferred to expedite the process and to ensure uniform moisture absorption.
Steaming
- To gelatinize the starch within the rice grains, making them harder and less prone to breakage during milling.
- The soaked paddy is exposed to steam in steam chambers or parboiling tanks.
- The steaming process typically lasts for 20-30 minutes, depending on the desired level of gelatinization.
- High pressure and temperature are maintained to ensure uniform steaming.
Drying
- To reduce the moisture content of the steamed paddy to around 14% for safe storage and milling.
- The drying can be done using sun drying, hot air dryers, or mechanical dryers.
- Initial rapid drying followed by slow drying to prevent cracking of the grains.
- Proper control is maintained to ensure even drying and to avoid damage to the rice grains.
Our Customers From Rice Mill Industry







Boiler Options for Rice Mill Industry


